This article was first published on the WeChat public account: Hedge Research and Research. The content of the article belongs to the author's personal opinion and does not represent the position of Hexun.com. Investors should act accordingly, at their own risk.
Cotton yarn futures will be available on August 18, 2017.
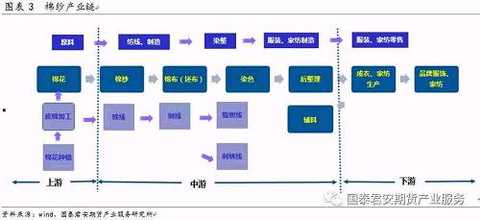
China is the world's largest cotton yarn producer, consumer and importer. The cotton textile industry is a traditional pillar industry of China's national economy and an important civilian production industry. The cotton textile industry is the basic industry of textiles. The product chain of cotton yarn can be briefly described as: cotton-cotton yarn-cotton-clothing home textile, and printing and dyeing and finishing in the middle. The direct producer of cotton yarn is cotton spinning mill. The cotton mill purchases cotton from upstream ginning mills or traders, processes and produces cotton yarn, sells it to downstream weaving mills or traders, and the end products are garment home textile products.
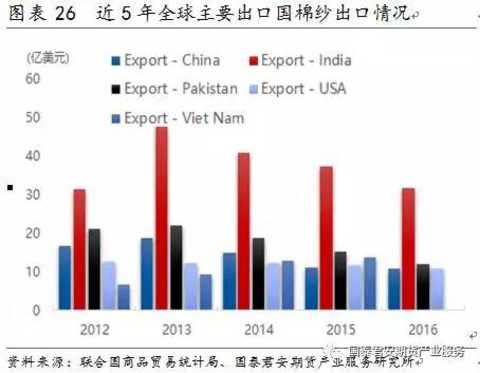
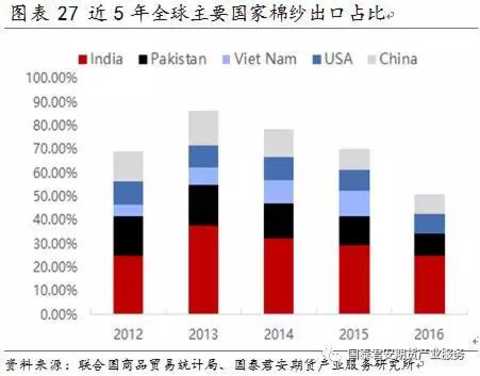
The annual output of cotton yarn is about 21 million tons. China, India, Australia and Pakistan are the world's major cotton yarn producing areas. The annual trade volume is about 3 million to 3.5 million tons. From the perspective of trade flows, China is a major cotton importer (the proportion of imports to the world). Up to 50%), the annual import volume is about 2 million tons. India is a major cotton exporter (exports account for about 25%-30% of the world), followed by Pakistan, Vietnam and the United States. China's cotton yarn imports from India, Pakistan and Yarn account for 60%-70% of the total imports. China's cotton yarn production is about 600-700 million tons, and the annual consumption is about 7-9 million tons. The gap between production and demand is supplemented by imports.
Domestic cotton yarn production and consumption are relatively concentrated, mainly concentrated in the central and eastern regions of China. Cotton yarn production areas include Shandong, Henan, Jiangsu, Hebei and Hubei, and its main consumption areas include Shandong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Henan and Guangdong.
There are many factors affecting the price fluctuation of cotton yarn. There are basically three types, namely supply factor, demand factor and other factors.
Supply factors include cotton supply and cost, cotton yarn start-up and profit, etc., which mainly affect costs and support cotton yarn prices. Under normal circumstances, the price of cotton yarn is more consistent with the trend of cotton. The raw materials of pure cotton yarn are all from cotton. The cotton yarn costs about 70% of the cotton yarn, and the rest is fixed cost. Although the short-term changes in the fixed processing cost will be small, the overall situation is still affected by factors such as cotton blending, labor, electricity bills, taxes, etc., and the cost of cotton blending on cotton yarn is also very large. Demand factors include downstream demand growth, corporate benefits, quantity and price of alternatives, etc., which mainly affect the level and fluctuation of cotton yarn prices. Other factors include logistics costs, macro environment, and cyclical factors.
Cotton yarn futures contract design focus points:
(1) The cotton yarn contract delivery month is from January to December, which is different from the existing cotton contracts 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, and November.
(2) The delivery target is 32 pure cotton yarns. Imported cotton yarn is not allowed to be delivered at the beginning of the market; after smooth operation, the imported cotton yarn will be released.
(3) There are two kinds of foreign fiber testing: test weaving test and yarn test. The former has a detection time of 1-2 days and costs 600-700 yuan/batch. The latter has a detection time of 1 hour and costs 150 yuan/batch. At the beginning of the cotton yarn futures market, the test weaving test method was used to detect the foreign fibers, and the feasibility of testing the foreign fiber by the yarn skein instrument was continued.
(4) The base of delivery is in Shandong, Henan and Jiangsu. Zhejiang is used as a cotton yarn auxiliary delivery site.
(5) Adopting factory delivery at the initial stage of the listing, and increasing warehouse delivery after smooth operation. The factory warehouse warehouse receipt must provide 120% bank guarantee or 100% cash.
(6) The warehouse receipts are valid for 4 months, and are cancelled in 2, 6, and October.
(7) On the 1st trading day of the delivery month, the standard warehouse receipts and non-standard warehouse receipts can be self-reported; on the 10th trading day, only the standard warehouse receipts can be delivered.
Text|Guotai Junan Futures Industry Service Editor | Hedge research and reprint, please indicate the source
01
table of Contents
1. Introduction to cotton yarn
1.1 Basic introduction of cotton yarn
1.2 cotton yarn classification
1.3 cotton spinning ring spinning process
1.4 Cotton yarn specifications and quality classification
1.4.1 Classification of cotton yarn specifications
1.4.2 Quality classification of cotton yarn
1.5 cotton yarn inspection standard
1.6 Cotton yarn packaging and storage requirements
1.7 cotton yarn industry chain
1.8 Domestic cotton yarn trade characteristics
1.9 China's yarn pattern
2. Cotton yarn supply and demand situation
2.1 Production aspects
2.1.1 Distribution of cotton yarn production areas
2.1.2 Low concentration of cotton yarn industry
2.1.3 Cotton yarn production capacity
2.2 Consumption aspects
2.2.1 Cotton yarn consumption
2.2.2 Main areas of domestic consumption
2.2.3 Cotton yarn consumption characteristics
2.3 Trade situation
2.3.1 Domestic trade flow of cotton yarn
2.3.2 International trade in cotton yarn
3. Analysis of the price of cotton yarn
3.1 Historical fluctuations in cotton yarn prices
3.2 Factors affecting cotton yarn prices
3.1.1 Supply factors
3.1.2 Demand factors
3.1.3 Other factors
4. Cotton yarn futures trading
4.1 Cotton yarn futures contract
4.2 Risk Management
4.2.1 Trading Margin System
4.2.2 Ups and downs system
4.2.3 Limit system
4.3 Delivery Rules
4.3.1 Delivery criteria
4.3.2 Delivery method
4.3.3 Delivery process
4.3.4 Delivery location
First, cotton yarn introduction
China is the world's largest cotton yarn producer, consumer and importer. Textile products are an important source of clothing consumption and living materials. The textile industry is the general term for the production of textile raw materials into clothing and other textiles. The cotton textile industry is the basic industry of textiles. Cotton yarn and cotton are used for clothing, home textiles and industry. The front products of knitwear, cotton yarns of different specifications and varieties are important links to support downstream development. The cotton textile industry is a traditional pillar industry of China's national economy and an important civilian production industry.
The domestic cotton textile industry is facing rapid development, fierce competition, rising labor costs and frequent fluctuations in raw material prices. In this context, cotton yarn futures will be escorted for textile companies.
Cotton yarn futures will be listed on August 18, 2017. This article will focus on the cotton yarn industry for investors' reference.
1.1 Basic introduction of cotton yarn
Yarn is a slender body made of a certain length of short fibers or filaments and having a certain strength and other physical and mechanical properties. Yarn is the basic unit that makes up the fabric.
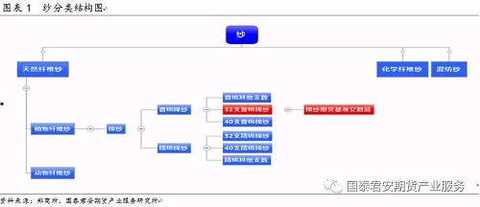
According to the different raw materials, the yarn can be divided into natural fiber (cotton, silk, hemp, wool) yarn, chemical fiber (polyester fiber, viscose fiber) yarn, and blended yarn.
Cotton yarn is a kind of natural fiber yarn. Its raw material is cotton. 95% of China's cotton consumption is used for spinning. Cotton belongs to the listed varieties of Zhengshang Institute. Cotton yarn is the most direct downstream product of cotton. It is a yarn that is processed into a woven fabric by a certain textile process. Chemical fiber is the main substitute for cotton yarn, including man-made fiber and synthetic fiber. The upstream raw materials for chemical fiber are PTA (fine terephthalic acid) and MEG (ethylene glycol). Animal fibers (silk, wool, down, etc.) and hemp fiber are also substitutes for cotton yarn, but the substitution effect is far less than that of chemical fiber.
Cotton yarn is the most basic material used for thread making and weaving. Most of the cotton yarn is used to produce all kinds of cotton cloth (also called grey cloth). After dyeing and processing, it is widely used in the end consumption field of home textiles, clothing textiles, industrial textiles, etc., and a small part is used to make sewing thread and embroidery thread.
|
1.2 Cotton yarn classification
The specifications of cotton yarns are very complicated and detailed. There are more than 700 kinds of yarns in the current category. Downstream fabric manufacturers often order cotton yarns according to the different needs of their products. Zhengshang Institute's cotton yarn benchmark delivery product is: 18.5tex (32 inches) carded cotton plain color single yarn (ring spinning).
1) According to the different yarns of yarn forming equipment, it is divided into ring spinning, air spinning (OE), siro spinning, compact spinning, vortex spinning, etc. The most common cotton yarns are generally ring spinning and air spinning. Line, Zhengshang Institute's cotton yarn delivery standard requires ring spinning. Ring spinning is made on a ring spinning machine by twisting with a traditional spinning method, which is relatively large in the current market.
2) The carded and combed yarns are divided according to the spinning process. The carded yarn is a yarn spun from a cotton fiber through a common spinning system, and the combed yarn is a yarn spun from a combed spinning system using cotton fibers. The combed yarn is made of high-quality raw materials, and the fibers in the yarn are straight and parallel, the knots are few, the gloss is good, the strips are even and the strength is high, and the cotton yarns are mostly used for weaving high-grade fabrics.
3) According to the use, it is divided into knitting yarn and woven (woven) yarn. The main difference between the two is the difference in twist. The yarn twist coefficient of knitting is less than 330, and the yarn twist coefficient of woven (woven) is greater than 360. .
4) According to different yarn dyeing and finishing, it is divided into natural yarn (primary yarn), dyed yarn, bleached yarn, color spinning yarn, mercerized yarn and singe yarn.
5) According to the different raw materials used, it is divided into pure cotton yarn and cotton blended yarn. Zhengshang Institute's cotton yarn benchmark is pure cotton yarn.
1.3 Cotton spinning ring spinning process
Zhengshang Institute's cotton yarn benchmark delivery product is: 18.5tex (32 inches) carded cotton plain color single yarn (ring spinning), mainly because of its largest market share, can provide sufficient physical security, and basically each Textile mills are able to produce. In addition, the transaction also loosens the restrictions on the delivery. The delivery products can be negotiated with the purchaser by means of self-reporting and discounting of other ring-spun cotton yarns, provided that the procurement company agrees and accepts the paired products. This section understands the process of cotton spinning ring spinning carding as follows:
1) Raw materials: use a variety of raw cotton. Make full use of the strengths of various raw cotton to meet the requirements of different yarns.
2) Open cotton: The main task is to loosen the bulk fiber into small pieces, initially remove large impurities, and mix the fibers of different grades and grades evenly. The process is: opening - removing impurities - mixing - uniform.
3) Carding: The process is: full combing - in addition to impurities and linters - mixing - uniform strips (strips).
4) Drawing: The main task is to increase the parallelism of the fibers and make the tampon into a roll with uniform weight and accurate weight. The process is: combining, drawing, mixing, and forming.
5) Roving: The process is: drafting-twisting-winding-forming.
6) Fine sand: The roving is drawn and twisted to form a spun yarn.
7) Post-processing: The main task is to remove coarse details, improve strength, wear resistance, dryness, and stable twist. The process is: winding-and-yarn-twisting.
8) The combing process has more combing steps after the draw. The procedure is: removing the short pile - removing the neps, impurities and defects - separating the fibers, straightening, paralleling - further mixing (and cooperating) into a strip.
|
1.4 Specifications and quality classification of cotton yarn
1.4.1 Classification of cotton yarn specificationsThe specification of cotton yarns is also very complicated, and the classification is particularly fine. Here, the index of the thickness of the yarn is indicated. There are two ways to describe the degree of thickness: one is the fixed length system (number system): expressed in terms of the weight of the yarn per unit length. One is the weight system: expressed in terms of the length of the yarn per unit weight. China currently stipulates the use of a fixed length system.
Fixed weight system:
- Inch Count (Ne) - Ne = Yarn Length Code / (840 * Yarn Weight Pounds)
- Metric count (Nm) - Nm = fiber or yarn length meters / weight grams
Fixed length system:
- Tex number - Ntex = (1000 * fiber or yarn weight grams) / length meters;
- denier (D) - Nden = (9000 * fiber or yarn weight grams) / length meters;
China's current general-purpose "English" type: one pound (454 grams) of heavy cotton yarn (or other component yarn), the length of 840 yards (0.9144 yards / meter), the fineness of the yarn is one. If a pound of yarn, its length is 10 × 840 yards, its fineness is 10, and so on. The larger the number in front of S, the thinner the yarn, and the lighter, thinner and softer the woven fabric. The smaller the number, the thicker the yarn and the heavier, thicker and rougher the woven fabric. Such as: 40s cotton yarn is thinner than 32s cotton yarn.
The cotton yarn of 17s and below is a coarse yarn, which is mainly used for weaving coarse cloth, flannel, sturdy and so on. 18-27s cotton yarn is a medium yarn used for weaving general fabrics such as plain cloth, twill cloth and satin. Cotton yarns of 28 and above belong to fine yarns, which are used for weaving fine cloth poplin, high-grade knitted fabrics, high-grade woven fabrics, and the like.
32S carded cotton color single bobbin (ring spinning) is the benchmark delivery of Zhengshang cotton yarn futures. 32S card can produce dozens of kinds of clothing (T-shirts, shirts, underwear, pants, socks, etc.). Production threshold, low technical content, relatively easy production, more alternative varieties, considering import concessions, import tariffs at 0-5% level, the market competition is greater.
1.1.2 Quality classification of cotton yarn
The quality grade of cotton yarn is similar to that of cotton. It is also in batches. The national standard "Cotton Color Yarn" (GB/T398-2008) issued by the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China stipulates that cotton yarns are produced in the same variety for one day and night. The quantity is a batch, the test is carried out according to the specified test period and various test methods, and the products of the cotton yarn are evaluated according to the results.
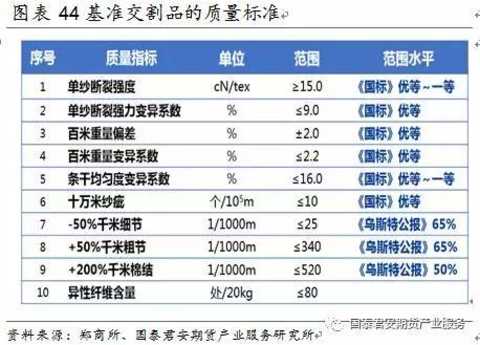
The products of cotton yarns are classified into superior, first-class, second-class, etc., and those below the second-class index are third-class. Cotton yarn products, such as single yarn breaking strength coefficient of variation, 100-meter weight variation coefficient, single yarn breaking strength, 100-meter weight deviation, strip uniformity, 1g inner cotton agglomeration number, 1g inner neps impurity total grain number, ten The lowest of the eight items of the ten thousand yarns.
1.5 Cotton yarn inspection standard
According to the national standard, the yarn quality is evaluated according to the quality index and the unevenness of the weight. The cotton yarn was rated according to the uniformity of the strip and the neps and the number of miscellaneous plasmids. The quality index mainly refers to the strength of the yarn, which reflects the durability and durability of the fabric to a certain extent. The grade of the yarn mainly reflects the difference in the thickness of the yarn and the appearance of the flaw. It directly affects the appearance of the fabric, such as the smoothness of the texture, the clarity and the size of the shadow. The quality of yarn is closely related to production management, process conditions, mechanical conditions, technical operation level, the quality of raw cotton and its reasonable use.
Please refer to GB/T398-93 national standard for technical specifications of cotton yarn.
Cotton yarn inspection method according to GB/T398-93 "cotton color yarn"; GB/T4743-95 "measurement method of yarn linear density (or count) - skein method"; SN/T0450-95 "export color Inspection rules for cotton yarns and combed polyester-cotton blended yarns.
Inspected according to the quality specifications and indicators specified in the trade contract.
1.6 Packaging and storage requirements for cotton yarn
Cotton yarn can be divided into cheese yarn and skein according to different molding. The inner packaging of the cotton yarn is a plastic bag with the name of the factory, the name and specifications of the product, the name of the registered trademark, the grade, the weight, the batch number, the package number, the number of the yarn and the date of the package.
The outer packaging of cotton yarn is mainly composed of carton or woven bag. The packaging should be neat, dry and strong, suitable for long-distance transportation.
The validity period of cotton yarn inspection is one year in the north and half a year in the south. If it exceeds the validity period, it must be inspected and checked for major items: mildew, insects, water stains, pollution, damage and so on.
In terms of warehousing, the cotton fiber has no change in properties after being processed into yarn, so the storage environment of cotton yarn is basically the same as that of raw cotton. When the cotton yarn is packaged, the actual moisture regain rate shall not be higher than 10.5%. If it exceeds the pile, the corresponding measures shall be taken to prevent mildew.
1.7 Cotton yarn industry chain The product chain of cotton yarn can be briefly described as: cotton-cotton yarn-cotton-clothing home textile, and printing and dyeing and finishing in the middle. The direct producer of cotton yarn is cotton spinning mill. The cotton mill purchases cotton from upstream ginning mills or traders, processes and produces cotton yarn, sells it to downstream weaving mills or traders, and the end products are garment home textile products.
|
1.8 Domestic cotton yarn trade characteristics
1) B2B mode: Both buyers and sellers of cotton yarn are merchants. The sellers are generally cotton mills and traders. The buyers are cotton factories and traders.
2) Fluctuation of raw materials: cotton yarn raw materials are all from cotton, prices fluctuate with cotton prices, and cotton prices fluctuate greatly.
3) Order-based procurement: SMEs are almost not stocked.
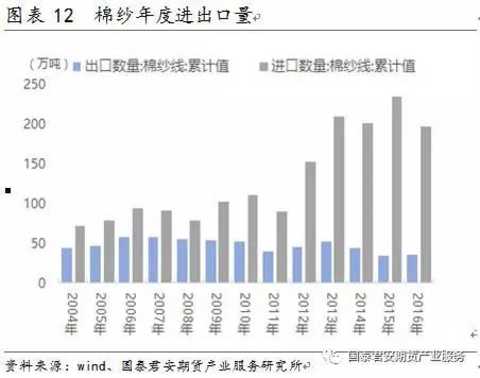
4) The proportion of cross-border purchases is about 20%: from the perspective of cotton yarn imports, the import tariffs from India and Pakistan are about 3.5%-5%, and the import tariffs from Vietnam are 0. The proportion of cotton yarn imports in China has increased year by year. As of 2016, net cotton yarn imports accounted for In the same period, the domestic consumption of cotton yarn is about 20%.
1.9 China's yarn pattern
China's cotton yarn production accounts for 33% of the yarn production, the main production areas are mainly concentrated in Shandong, Henan, Hebei and Jiangsu; chemical fiber yarn production is concentrated in Fujian, Jiangsu, Zhejiang and other places.
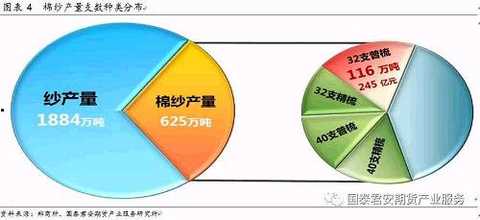
China's cotton yarn production of combed yarns accounted for about 35%, showing a continuous improvement trend, and the production structure gradually shifted to high-count comb products. In the distribution of the overall cotton yarn yarn structure, the C32S yarns of the upcoming cotton yarn futures products account for about 22% of the total, accounting for a high proportion, with the most extensive application, with an annual output of 100-1.2 million tons. The proportion of JC40s yarn is about 10%-13%.
|
At present, the annual demand for cotton yarn in China is about 7 million to 9 million tons, the output is about 6 million tons, the annual import volume is 2 million tons, the annual export volume is about 300,000-400,000 tons, and the net cotton yarn imports account for about the total consumption. It is 20%. At present, China's imported yarns are dominated by low-end carding, and most of the exported cotton yarns are combed yarns. Among them, imported cotton yarns accounted for the largest proportion of Indian cotton yarn, Pakistan cotton yarn and Vietnamese cotton yarn. The cotton yarn imported from these three countries accounted for 60%-70% of the total import volume.
Second, cotton yarn supply and demand situation
2.1 Production aspects
The raw material for pure cotton yarn production is cotton, and 95% of China's cotton consumption is used for spinning. The production of domestic cotton yarn corresponds to the demand for cotton.
Before and after 2000-2008, it was the "golden development period" of China's textile and garment industry. After 2008, affected by the economic downturn and industrial migration, the overall demand of the textile industry has shrunk. The demand for cotton and cotton yarns has also been replaced by chemical fiber, and cotton consumption has continued to decrease, indicating that domestic cotton yarn production has also decreased.
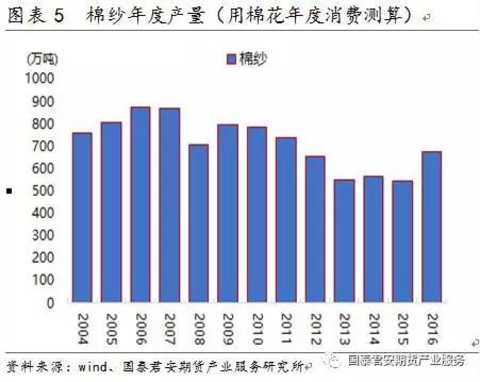
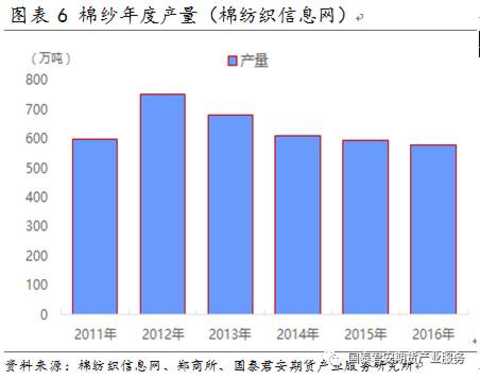
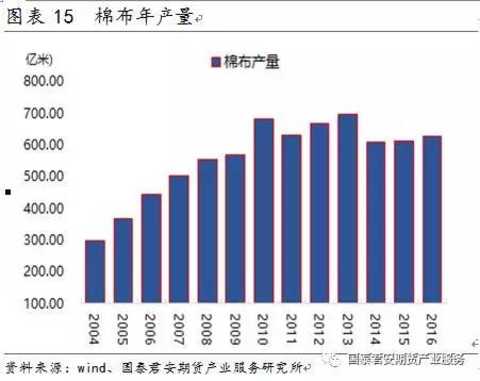
At present, the Bureau of Statistics does not directly publish China's cotton yarn production data, and uses cotton annual consumption to calculate cotton yarn production. As shown in Figure 5, cotton yarn production has declined year by year since 2010. The current annual output of cotton yarn is about 6-7 million tons.
|
|
2.1.1 Distribution of cotton yarn production areas
The production and consumption of cotton yarn is relatively concentrated, mainly concentrated in the central and eastern regions of China.
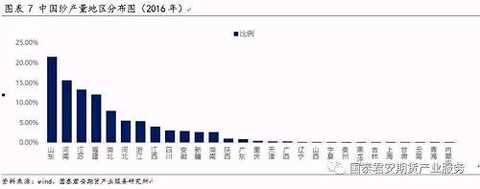
China's yarn production provinces are mainly concentrated in East China and Central China. Since the central labor cost is lower than that of the coastal areas, the cotton spinning capacity in the coastal areas has shifted to the central part in recent years, and the output of Fujian yarn has increased. In the past 10 years, Shandong, Henan, and Jiangsu have maintained the top three positions in the country, Shandong ranks first, followed by Henan, Jiangsu again, and the three provinces account for more than 50% of the country. In addition, Fujian, Hubei, and Zhejiang are also important. The yarn production province.
The proportion of output in Shandong and Jiangsu provinces has declined in recent years, and the proportion of output in Henan has increased. The proportion of the three provinces in the country has remained above 50%. In 2016, Shandong accounted for 21.49%, Jiangsu accounted for 13.29%, Henan accounted for 15.57%, and Fujian accounted for 12%.
|
2.1.2 Low concentration of cotton yarn industry
In terms of the scale of cotton yarn enterprises, enterprises with a production capacity of less than 50,000 spindles in China can be considered as small enterprises, and enterprises with a capacity of 50,000 spindles and 200,000 spindles are medium-sized enterprises, and large-scale enterprises with a scale of 200,000 spindles or more. According to the data of China Cotton Textile Industry Association, there were 8,300 cotton textile scale enterprises in 2014, and more than 9,000 in 2013, 90% of which were private enterprises. The industrial concentration was low, and the top 100 cotton textile enterprises only accounted for 30%, reflecting the enterprise. The characteristics of a large number and low industrial concentration.
2.1.3 Cotton yarn production capacity
China is currently the country that produces the largest amount of cotton yarn and cotton yarn. The spinning capacity (120 million spindles) is also the world's number one, accounting for about 40% of the world's production capacity.
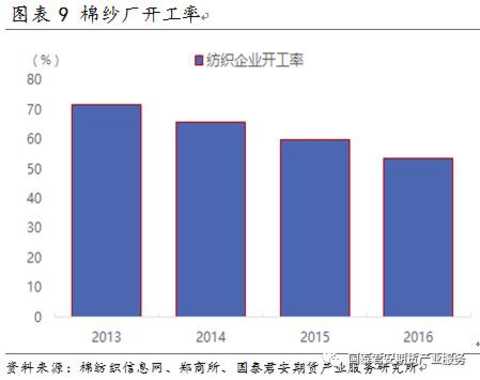
Due to factors such as rising production capacity, falling demand and national policies, the operating rate of China's textile industry has shown a volatility decline in recent years, and overcapacity is still relatively serious. In 2013, the operating rate of cotton yarn mills in China reached 70%, and then fell back. In 2016, the operating rate fell to around 55%.
|
|
2.2 Consumption aspects
2.2.1 Cotton yarn consumptionAt present, the Bureau of Statistics does not directly publish cotton yarn consumption data. The actual consumption data is uncertain. The industry tends to use apparent consumption (yield + import-export) to replace it. The output of cotton yarn directly downstream cotton can also reflect cotton yarn. Consumption situation.
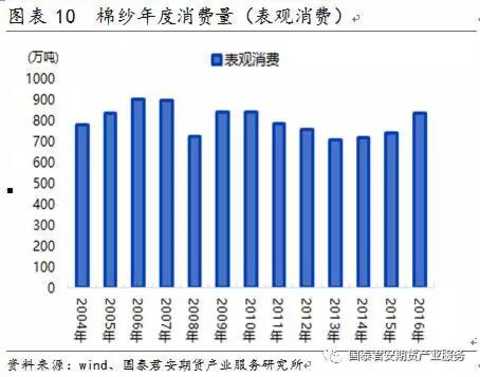
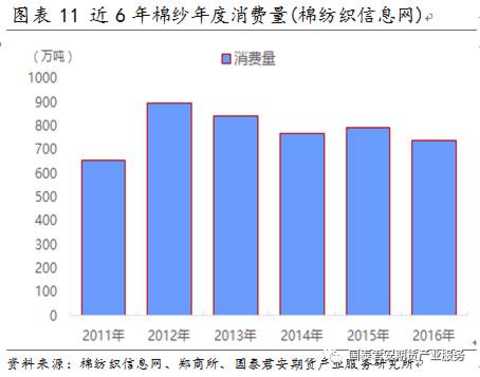
The consumption of cotton yarn has been decreasing since 2010. The overall consumption of cotton yarn is about 7-9 million tons.
The proportion of cotton yarn imports in China has increased year by year. 13 years ago, the domestic implementation of the policy of purchasing and storage, each ton of cotton is more than 5,000 yuan more expensive than foreign countries, cotton yarn raw material is cotton, different from cotton import quota, cotton yarn has no quota restrictions, which directly leads to a large number of foreign low-priced cotton yarn into the Chinese market (The import tariffs from India and Pakistan are about 3.5%-5%, and the import tariffs from Vietnam are 0.) The proportion of cotton yarn imports in China has increased year by year. As of 2016, net cotton yarn imports accounted for about 20% of the domestic consumption of cotton yarns in the same period. .
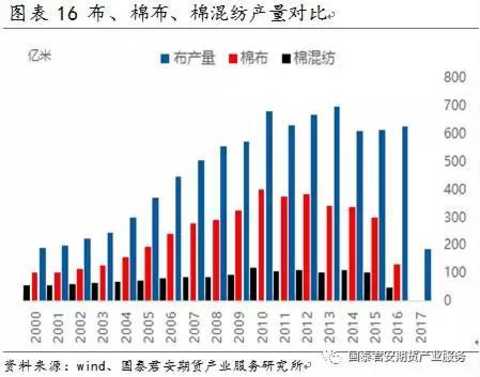
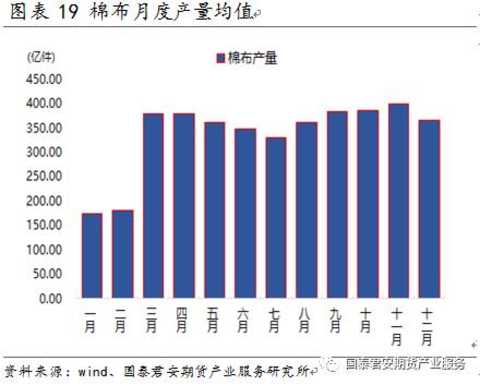
In addition, due to the low price of chemical fiber, the substitution effect of cotton yarn has been enhanced, and the proportion of cotton in the cloth has also gradually decreased since 2012 (as shown in Figure 16). The proportion of textile cotton is gradually increased from the highest of 560%. Drop to a level of twenty percent.
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.2.2 Main areas of domestic consumption
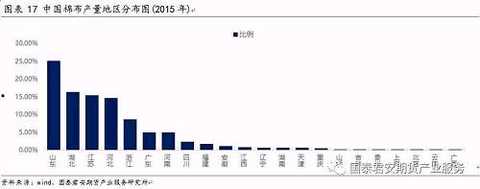
China's cotton production provinces are mainly concentrated in East China and Central China. In recent years, the province of cotton production has expanded from Shandong to other coastal areas, and the proportion of cotton production in Hubei has also increased. Shandong, Hubei, Jiangsu, Hebei, the four provinces accounted for more than 70% of the national cotton production, specifically by 2015, Shandong accounted for 25.13%, Hubei accounted for 16.27%, Jiangsu 15.43%, Hebei accounted for 14.64%, Zhejiang accounted for 8.64% .
|
2.2.3 Characteristics of cotton yarn consumption
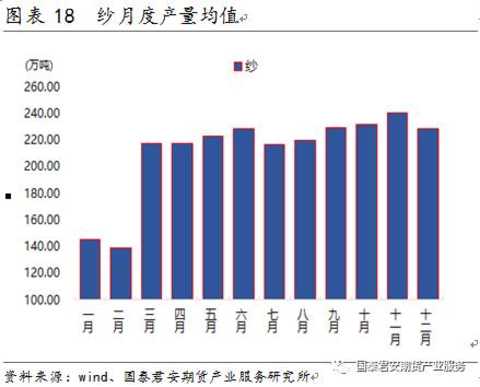
Relative to the production of cotton yarn, the seasonality of cotton yarn consumption is more obvious. There are light seasons: in general, May-August and December-February are the off-season of cotton yarn demand, while September-November is the peak season, 3- April is its small peak season, and there are gold, nine, and silver in the market.
|
|
2.3 Trade situation
2.3.1 Domestic trade flow of cotton yarnCotton yarn production areas include Shandong, Henan, Jiangsu, Hebei and Hubei, and its main consumption areas include Shandong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Henan and Guangdong. In addition to self-selling, Shandong, Jiangsu and Henan cotton yarns flow to coastal areas such as Zhejiang, Guangdong and Fujian. Other major producing provinces set up distribution points in cotton textile enterprise clusters in Jiangsu and Zhejiang, and the terminal flows are mostly in coastal areas such as Zhejiang, Guangdong and Fujian.
In general, cotton yarn production areas (Shandong, Henan, Jiangsu, Hebei, Hubei) may have a certain need to sell hedging, cotton yarn sales areas (Zhejiang, Shanghai, Shandong, Hubei, Guangdong, Fujian) or there are certain buying sets Guarantee demand.
2.3.2 International trade in cotton yarn
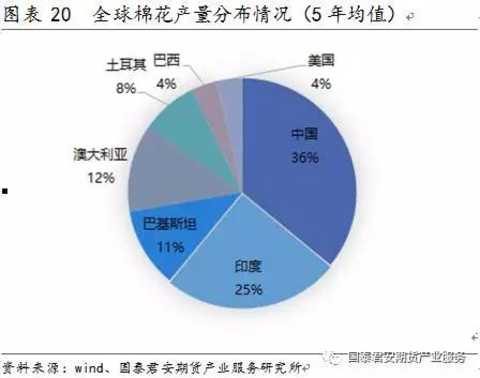
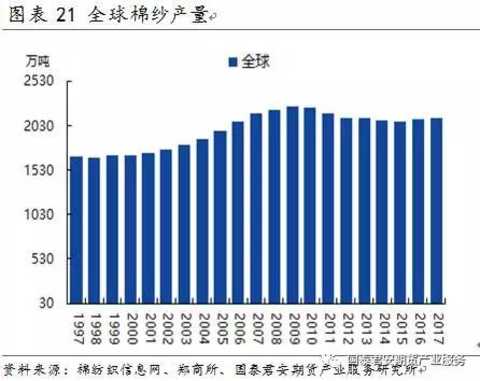
The raw material for cotton yarn production is mainly cotton, and the global cotton yarn production area can be calculated by the distribution of cotton consumption. The annual global output of cotton yarn is about 21 million tons. China, India, Australia and Pakistan are the major cotton yarn producing regions in the world. The cotton yarn production accounts for 36%, 25%, 12% and 11% respectively.
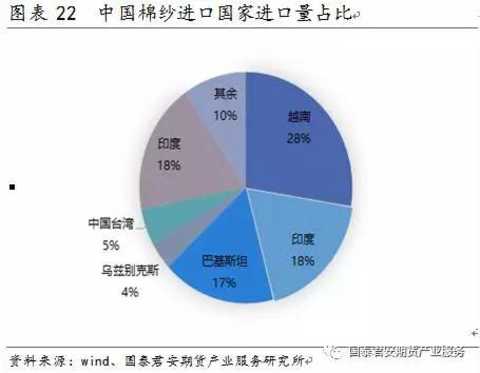
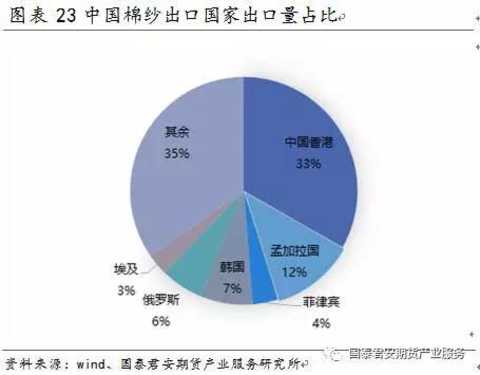
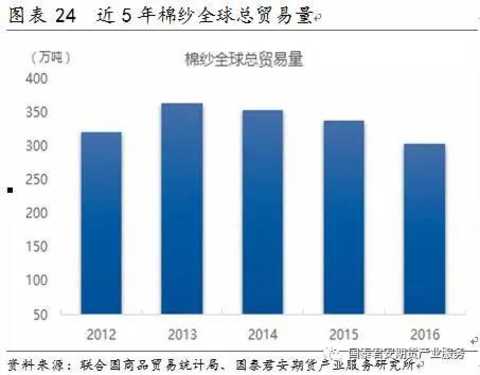
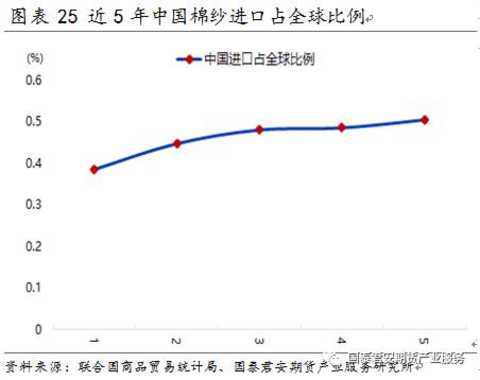
In the past five years, the total annual trade volume of cotton yarns in the world is between 3 million and 3.5 million tons. In 2016, the total global trade volume was about 3.3 million tons. From the perspective of trade flows, China is a major cotton importer (the import volume has reached 50% globally). India is a major cotton exporter (exports account for about 25%-30% of the world), followed by Pakistan, Vietnam and the United States. Vietnam, India and Pakistan are the world's major exporters. China's imports of cotton yarn from India, Pakistan and Vietnam account for 60%-70% of total imports. In 2016, China's imports from these countries were 28%, 18% and 17% respectively. Zhengshang currently stipulates that imported cotton yarn cannot enter the futures market as a delivery product.
Pakistan mainly produces medium and low-weight cotton yarns. The cotton yarns exported to China are mainly low-yarn yarns, towel yarns and siro spinning yarns. Basically, they are all C21S and below yarns. For the time being, the impact on domestic market is not in 32 or more markets. Big. In recent years, India has developed rapidly in the middle and low count yarn market, and gradually developed high count yarns. It not only has price advantage, but also gradually improves and improves quality and stability. China's cotton yarn imported from India is mainly medium and high count yarn. It mainly includes specifications such as C21, C32S, C40S, JC32S, and JC40S. India is the biggest competitor in China's domestic cotton spinning industry. Its industrial chain is gradually developing and perfecting. The quality of domestic cotton is good and the spinning equipment is advanced. There is no cotton in Vietnam. The raw materials are basically imported. At present, one third of the domestic yarn mills are invested abroad. Many large Chinese companies invest in it, producing more than 80% of cotton yarn and then selling it back to China, and the price advantage is obvious. The cotton yarn exported to China by Vietnam is also dominated by medium and high branches. When analyzing imported yarns, attention should be paid to the situation of Vietnamese and Indian yarns.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Third, the price analysis of cotton yarn
3.1 Historical fluctuations in cotton yarn prices
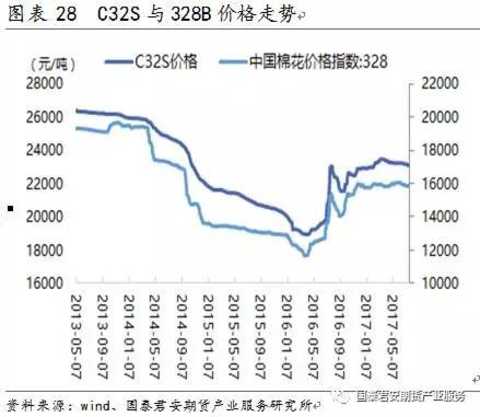
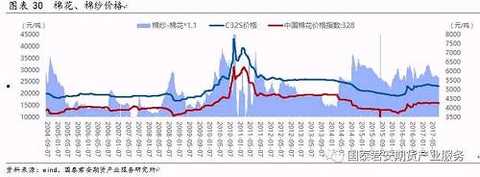
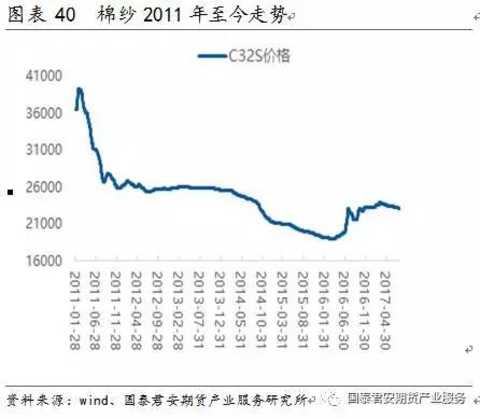
The price of cotton yarn fluctuated greatly. From January 2013 to July 2017, the domestic C32S price fluctuated between 18,000 and 27,000 yuan/ton, with the maximum fluctuation range of 50%. Among them, the domestic C32S price fluctuated between 22,900 and 23,500 yuan/ton in the first half of 2017, with a fluctuation range of 18.7%. The average price in the first half of 2017 was about 23,187 yuan/ton.
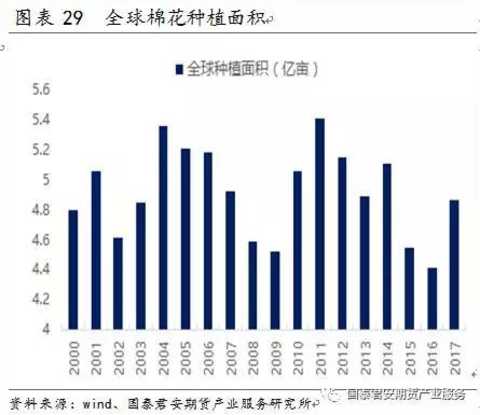
Cotton prices have a leading role in cotton yarn price trends. The cotton yield is positively related to the cotton planting area. The cotton planting area has obvious cyclical characteristics in the past 20 years, the 5-year slow decline period (2005-2009, 2012-2016), and the 2-year rapid recovery period (2003-2004, 2010). -2011). According to the above-mentioned cotton production expansion cycle, the 2017-2018 cotton is in a high probability of expansion. In 2017, domestic cotton is already in the expansion cycle: the latest USDA report on August 11th said that the expansion of China's cotton production in 2017/2018 is expected to be 7.69%, and the expansion of cotton outside China is 10.83%. In addition, the stock of domestic reserve cotton remains Larger need to continue to the library. Under the loose supply background, the current demand for cotton yarn and cotton orders is generally stable and weak. It is expected that cotton prices will be under full pressure during the year, and cotton yarn prices are also expected to be weak.
|
|
3.2 Factors affecting cotton yarn prices
There are many factors affecting the price fluctuation of cotton yarn. There are basically three types, namely supply factor, demand factor and other factors.
3.2.1 Supply factors
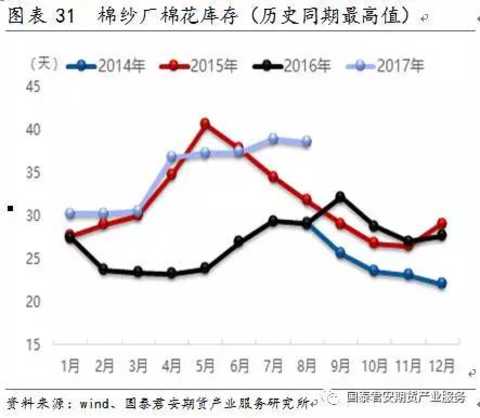
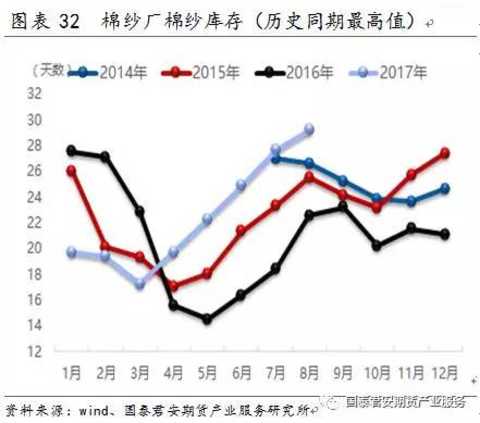
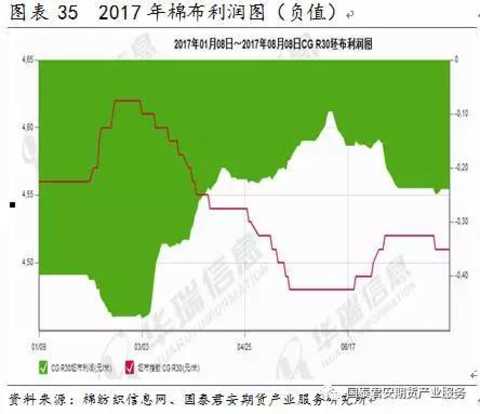
Supply factors include cotton supply and cost, cotton yarn enterprise start-up and inventory, etc., which mainly affect the cost of cotton yarn and have a supporting effect on cotton yarn prices.
Under normal circumstances, the price of cotton yarn is more consistent with the trend of cotton, and the correlation between cotton yarn and cotton price is 0.98.
Cotton yarn production cost = cotton * (1 + processing loss rate (take 10%)) + processing costs.
The raw materials of pure cotton yarn are all from cotton. The cotton yarn costs about 70% of the cotton yarn, and the rest is fixed cost. Although the short-term changes in fixed processing costs will be small, the overall situation is still affected by factors such as cotton blending, labor, electricity bills, taxes, etc. The cost of cotton blending on cotton yarns is also very large. The cotton yarns of the same yarns on the market are different. Cotton, the difference of up to 1,000 yuan per ton.
From the spot price comparison, the cotton yarn price follows the fluctuation of cotton price. When the cotton shows rapid trend fluctuation, the cotton yarn has a certain lag, which may be related to the cotton mill inventory management.
1) In the process of rapid decline in cotton prices, such as 2014, because the price of the previous inventory may not be low, the price of cotton yarn does not immediately fall, and the price difference between cotton yarn and cotton has a process of rising and then decreasing.
2) During the rapid rise of cotton prices, such as 2010, because the price of the previous inventory may not be high, the price of cotton yarn does not immediately follow the rise, and the price difference between cotton yarn and cotton has a process of first restraining and then rising.
From the current spot price performance, the cotton yarn offer is relatively slow to change the cotton price. The current spot situation only reflects the commodity attributes of cotton yarn and does not reflect financial attributes. After the cotton yarn went on the market, after a round of complete delivery and the transaction matured, it is expected that the financial properties of cotton yarn futures will gradually reflect, and the time lag effect of cotton yarn futures relative to cotton futures price changes will be weakened. For example, changes in US cotton quickly affected domestic cotton prices, rather than affecting domestic cotton price changes after US cotton shipments to Chinese ports.
|
|
|
|
|
3.1.2 Demand factors
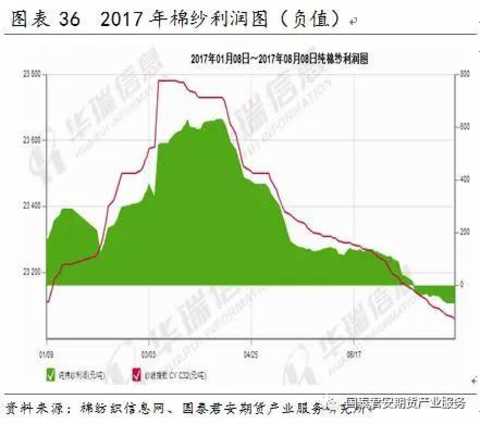
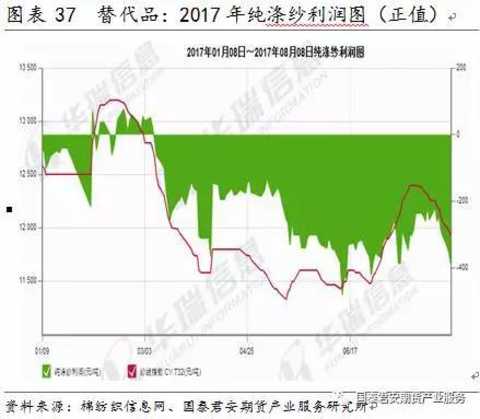
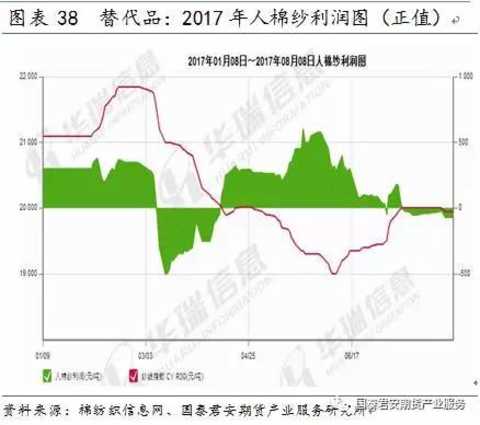
Demand factors include downstream (cotton, apparel and textile) demand growth, corporate benefits, alternatives quantity and price, etc., mainly affecting the level and fluctuation of cotton yarn prices.
Overall, the demand for domestic cotton industry chain has been sluggish in recent years. After 2010, the growth rate of domestic cotton demand has slowed down. The main reason is the weak internal and external demand for textiles and garments, and the impact of the chemical fiber fiber industry chain. After 2015, the global cotton production and demand gap began to appear, but large-scale destocking still has a restraining effect on prices.
In the short term, the profit of cotton yarn and cotton fabric is still falling and negative. The profit of cotton yarn substitute pure polyester yarn and human cotton yarn is positive, and the cotton chain is still in a weak state.
|
|
|
|
3.1.3 Other factors
Other factors include logistics costs, macro environment, government policies, etc., and also have a certain impact on the trend of cotton yarn futures.
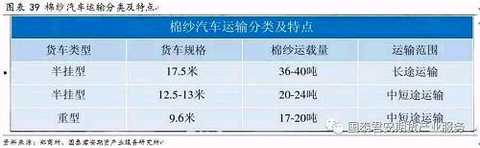
The main transportation tool for cotton yarn is truck transportation. The sales radius of cotton yarn can reach more than 800 kilometers. At this stage, the long-distance transportation cost of cotton yarn over 800 kilometers is about 400 yuan/ton, and the short-distance transportation cost within 800 kilometers is 70-300 yuan/ton. The flow of cotton yarn is mainly from the central part (Shandong, Henan, Jiangsu) to the coast (Zhejiang, Guangdong, Fujian).
The main cotton producing areas are well-connected and have good transportation capacity. However, there will be a certain degree of transportation tension from the inland transportation to the coastal season during the ripening season. When the capacity is tight, the freight rate will increase, which will support the cotton yarn price. In addition, Xinjiang is the main cotton producing area. In October and December each year, cotton will emerge from the Xinjiang to the Mainland, and there will be a certain degree of capacity tension. This will indirectly affect the price of cotton yarn.
|
In addition, cotton yarn is an intermediate link in the textile industry. The entire textile industry is a labor-intensive industry, and the cotton yarn industry is also affected by the macro environment. Economic policies related to cotton yarn (agricultural policy, foreign trade policy, financial policy, securities policy), industrial policies (cotton dumping policy, subsidy policy, textile import and export policy) will also have an impact on cotton yarn futures prices.
|
|
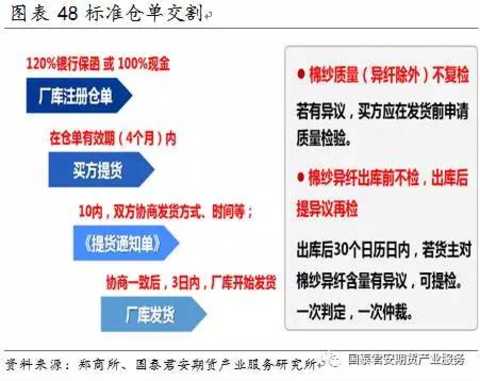
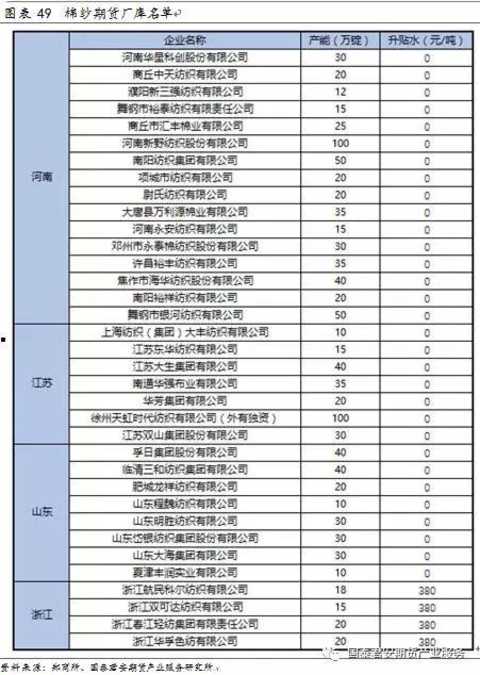
Fourth, cotton yarn futures trading 4.1 Cotton yarn futures contract Cotton yarn futures contract design focus points: (1) The cotton yarn contract delivery month is from January to December, which is consistent with the domestic industrial product futures delivery month, which is generally designed for consecutive months, different from the existing cotton contracts 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, and November. (2) The delivery target is 32 pure cotton yarns. Imported cotton yarn is not allowed to be delivered at the beginning of the market; after smooth operation, the imported cotton yarn will be released. (3) There are two kinds of foreign fiber testing: test weaving test and yarn test. The former has a detection time of 1-2 days and costs 600-700 yuan/batch. The latter has a detection time of 1 hour and costs 150 yuan/batch. At the beginning of the cotton yarn futures market, the test weaving test method was used to detect the foreign fibers, and the feasibility of testing the foreign fiber by the yarn skein instrument was continued. (4) The base of delivery is in Shandong, Henan and Jiangsu. Zhejiang is used as a cotton yarn auxiliary delivery site. (5) Adopting factory delivery at the initial stage of the listing, and increasing warehouse delivery after smooth operation. The factory warehouse warehouse receipt must provide 120% bank guarantee or 100% cash. (6) The warehouse receipts are valid for 4 months, and are cancelled in 2, 6, and October. (7) On the 1st trading day of the delivery month, the standard warehouse receipts and non-standard warehouse receipts can be self-reported; on the 10th trading day, only the standard warehouse receipts can be delivered. 4.2 Risk Management 4.2.1 Trading Margin System (1)一般月份最低交易ä¿è¯é‡‘设置为åˆçº¦ä»·å€¼çš„5%。 (2ï¼‰ä¸´è¿‘äº¤å‰²æœŸæ—¶ï¼Œäº¤æ˜“æ‰€æ ¹æ®ä¸åŒæ—¶é—´æ®µè°ƒæ•´äº¤å‰²æœˆåˆçº¦ä¿è¯é‡‘。 棉纱å“ç§ä¸´è¿‘交割月的ä¿è¯é‡‘梯度设计设置方法:棉纱期货åˆçº¦ä»Žäº¤å‰²æœˆä»½å‰ä¸€ä¸ªæœˆçš„第16个日历日起,ä¿è¯é‡‘æ高至10%,从交割月首个交易日起æ高至20%。 4.2.2 涨跌åœæ¿åˆ¶åº¦ (1)一般月份涨跌åœæ¿å¹…度为上一交易日结算价的4%。上市首日涨跌åœæ¿ä¸º8%。 (2)当棉纱期货åˆçº¦å‡ºçŽ°è¿žç»åœæ¿æ—¶ï¼Œäº¤æ˜“所将æ高涨跌åœæ¿å¹…度和ä¿è¯é‡‘水平。出现第一个åœæ¿å½“天结算时起,åˆçº¦çš„交易ä¿è¯é‡‘调整为9%,其åŽç¬¬ä¸€ä¸ªäº¤æ˜“日的åœæ¿å¹…度调整至7%;若第二天出现åŒæ–¹å‘åœæ¿ï¼Œç»“ç®—ä¿è¯é‡‘按照åˆçº¦ä»·å€¼çš„12%收å–,其下一个交易日的åœæ¿å¹…度调整至10%。 4.2.3 é™ä»“制度 棉纱期货æŒä»“é™é¢éµå¾ªä»¥ä¸‹åŽŸåˆ™ï¼š 棉纱期货é™ä»“制度设计å‚考已有å“ç§åšæ³•ï¼š (1)对期货公å¸ä¸é™ä»“,对éžæœŸè´§å…¬å¸ä¼šå‘˜å’Œå®¢æˆ·é™ä»“ï¼› (2)对一般月份é™ä»“从宽,对交割月份é™ä»“从严。 - åˆçº¦æŒ‚牌至交割月å‰ä¸€ä¸ªæœˆç¬¬15个日历日é™ä»“10000手; - 交割月å‰ä¸€ä¸ªæœˆç¬¬16个日历日至最åŽä¸€ä¸ªæ—¥åŽ†æ—¥é™ä»“1000手。 - 交割月é™ä»“200手,从严控制,防范交割月风险。 4.3 交割细则 4.3.1 äº¤å‰²æ ‡å‡† 基准交割å“:符åˆéƒ‘商所棉纱期货交割质é‡æ ‡å‡†çš„18.5tex(32英支)普梳棉本色ç’åå•çº±ï¼ˆçŽ¯é”纺)。 普梳C32Sç›®å‰å®šä¸ºæ£‰çº±æœŸè´§çš„äº¤æ˜“æ ‡çš„ç‰©ä»¥åŠåŸºå‡†äº¤å‰²å“,主è¦åŽŸå› 是其是公认行业定价基准ã€å¤§éƒ¨åˆ†çººç»‡åŽ‚都å¯ä»¥ç”Ÿäº§ã€å¸‚场份é¢æœ€å¤§ã€å…¶é…棉æˆåˆ†ä¸Žæ£‰èŠ±æœŸè´§åŸºå‡†äº¤å‰²å“相一致。æ¤å¤–郑商所在交割环节也放宽了é™åˆ¶ï¼Œäº¤å‰²å“å¯ç”¨å…¶ä»–环é”纺棉纱通过自报å‡è´´æ°´çš„æ–¹å¼å’Œé‡‡è´æ–¹è¿›è¡Œå商替代,å‰æ是采è´ä¼ä¸šåŒæ„并接å—é…对产å“。棉纱的å„é¡¹æŒ‡æ ‡ä¸ï¼Œé™¤äº†çº¿å¯†åº¦ä»¥å¤–,é…棉ã€å•çº±çš„æ–裂强度ã€æ¡å¹²å‡åŒ€åº¦ã€å¼‚纤å«é‡ä»¥åŠç²—细节ç‰éƒ½æ˜¯ä¸‹æ¸¸ä¼ä¸šæ¯”较看é‡çš„。 æ ¹æ®æ£‰çº±äº¤å‰²é€‚ç”¨çš„å›½å®¶æ ‡å‡†åŠã€Šå…³äºŽå¾è¯¢æ£‰çº±æœŸè´§åˆçº¦å’Œè§„则制度æ„è§çš„公告》细则规定准如下所示。 1)基准交割å“:18.5tex(32英支)普梳棉本色ç’åå•çº±ï¼ˆçŽ¯é”纺); 2)3ä¸ªåŸºæœ¬å±žæ€§æŒ‡æ ‡ã€10个质é‡æŒ‡æ ‡ï¼› 3)å¼•ç”¨æ ‡å‡†ï¼šã€Šæ£‰æœ¬è‰²çº±çº¿ã€‹GB/T 398-2008ã€ä¹Œæ–¯ç‰¹å…¬æŠ¥2013ã€ã€Šæ£‰çº±æœŸè´§å¼‚纤纤维检验规范》。 棉纱期货对交割货物的异性纤维å«é‡åšäº†è§„定,并设置åˆç†çš„替代交割范围åŠè´´æ°´å¹…度,如下表所示。棉纱仓å•å¼‚纤处ç†ï¼šäº§åº“仓å•äº¤å‰²+投诉处ç†æœºåˆ¶+异纤检验规范,如下表所示。 4.3.2 äº¤å‰²æ–¹å¼ æ£‰çº±æœŸè´§ä¸Šå¸‚åˆæœŸå®žè¡ŒåŽ‚库交割;待市场平稳è¿è¡ŒåŽï¼Œé€‚æ—¶å¯ç”¨ä»“库交割。 现阶段我国棉纺织ä¼ä¸šå¤šä»¥è®¢å•ç”Ÿäº§ï¼ŒçŽ°è´§è´¸æ˜“çš„ä¸è½¬ä»“储é‡åŠçººç»‡ä¼ä¸šåº“å˜è¾ƒä½Žã€‚在æ¤èƒŒæ™¯ä¸‹å®žè¡ŒåŽ‚库交割优势如下: (1)å¯æ供供货方基准交割å“åŠæ›¿ä»£äº¤å‰²å“以外的å“ç§è§„æ ¼ï¼Œæ»¡è¶³å…¶ä¸ªæ€§åŒ–çš„äº¤å‰²éœ€æ±‚ï¼Œé—´æŽ¥æ‰©å¤§äº¤å‰²å“ç§èŒƒå›´ï¼› (2)通过厂库æ供银行ä¿å‡½æˆ–其他交易所认å¯çš„æ‹…ä¿å½¢å¼å½¢æˆä»“å•ï¼Œä¸éœ€è¦æå‰å°†è´§ç‰©ç”Ÿäº§å‡ºæ¥ï¼Œå‡å°‘ä¼ä¸šèµ„金åŠèµ„æºå 用; (3)å‡å°‘入库环节,é™ä½Žäº¤å‰²æˆæœ¬ï¼› (4)利于ä¿éšœæœŸè´§äº¤å‰²å®‰å…¨ï¼Œé˜²èŒƒäº¤å‰²é£Žé™©ã€‚ 仓库交割备用,则å¯ä¸ºåŽæœŸè¿›å£æ£‰çº±å‚ä¸Žäº¤å‰²åˆ›é€ æ¡ä»¶ã€‚ 4.3.3 交割æµç¨‹ 1)在交割月å‰ï¼šäº¤å‰²å“以外的棉纱å¯é€šè¿‡æœŸè½¬çŽ°å®Œæˆå®žç‰©è´é”€ã€‚自åˆçº¦æŒ‚牌上市起,å–æ–¹ã€ä¹°æ–¹å‡å¯é€šè¿‡â€œæœŸè´§è½¬çŽ°è´§â€å¹³å°ï¼Œå¯¹å¤šè§„æ ¼ã€å¤šç‰çº§çš„棉纱进行需求匹é…;匹é…æˆåŠŸçš„,买å–åŒæ–¹ç¾è®¢â€œæœŸè½¬çŽ°â€å议,交易所对其相应æŒä»“以åŒæ–¹çº¦å®šçš„ä»·æ ¼è¿›è¡Œå¹³ä»“ï¼›ä¹°å–åŒæ–¹å商完æˆè´§ç‰©äº¤æ”¶åŠè´§æ¬¾ç»“算。 2)进入交割月:第1-9个交易日间,å¯è‡ªæŠ¥å‡è´´æ°´äº¤å‰²ï¼Œå¯æ ‡å‡†ä»“å•äº¤å‰²ã€‚ 交割å“以外的棉纱å¯é€šè¿‡è‡ªæŠ¥å‡è´´æ°´å®Œæˆäº¤å‰²ã€‚ å–方:æ¯äº¤æ˜“14:30å‰ï¼Œæ交éžæ ‡å‡†ä»“å•æ£‰çº±çš„ä¿¡æ¯åŠå‡è´´æ°´ï¼ˆä¸ºæŽ§åˆ¶äº¤å‰²é£Žé™©ï¼Œéœ€ä¸ºåŽ‚库棉纱)。 买方交割å“应情况: 交割å“应:é—市åŽäºˆä»¥é…对,å‡è´´æ°´æŒ‰å–方公布执行。 未å“应:é—市åŽäºˆä»¥æ’¤é”€ï¼Œå–æ–¹å¯äºŽæ¬¡æ—¥ç»§ç»æ交申请。 3)第10个交易日:åªå…è®¸æ ‡å‡†ä»“å•äº¤å‰²ï¼Œä¿æŒäº¤å‰²çš„一致性。 4.3.4 交割地点 (1)交割区域选择交通便利的主产区 ç›®å‰çš„交割地点主è¦åœ¨å±±ä¸œã€æ²³å—ã€æ±Ÿè‹ä¸‰çœï¼Œå¦å¤–有一个辅助交割地:浙江,å‚考è¿è´¹è®¾ç½®å‡è´´æ°´ã€‚ 棉纱的生产和消费地相对集ä¸ï¼Œä¸»è¦é›†ä¸åœ¨æˆ‘国的ä¸ä¸œéƒ¨åœ°åŒºã€‚棉纱产地包括山东ã€æ²³å—ã€æ±Ÿè‹ã€æ²³åŒ—和湖北ç‰åœ°ï¼Œè€Œå…¶ä¸»è¦æ¶ˆè´¹åœ°åŒ…括山东ã€æ±Ÿè‹ã€æµ™æ±Ÿã€æ²³å—和广东ç‰åœ°ã€‚山东ã€æ±Ÿè‹å’Œæ²³å—棉纱除自销外,æµå‘浙江ã€å¹¿ä¸œã€ç¦å»ºç‰æ²¿æµ·åœ°åŒºã€‚其他主产çœä¼ä¸šå¤šåœ¨æ±Ÿè‹ã€æµ™æ±Ÿç‰åœ°çš„棉纺织ä¼ä¸šé›†ç¾¤å¤„设置ç»é”€ç‚¹ï¼Œç»ˆç«¯æµå‘多为浙江ã€å¹¿ä¸œã€ç¦å»ºç‰æ²¿æµ·åœ°åŒºã€‚我国山东ã€æ²³å—ã€æ±Ÿè‹å’Œæµ™æ±Ÿæ£‰çº±äº§é‡ã€æ¶ˆè´¹å 比åˆå¹¶è¾¾åˆ°55%。2015年,交割地全国百强ä¼ä¸šæ•°ç›®è¾¾åˆ°69家,具有较强代表性。 å› æ¤ï¼Œéƒ‘商所考虑棉纱的主产地和主消费地,将棉纱的基准交割地设在山东ã€æ²³å—和江è‹ï¼Œæµ™æ±Ÿè®¾ä¸ºè¾…助交割地。 (2)交割厂库选择主è¦ç”Ÿäº§çœä»½çš„é‡ç‚¹ç”Ÿäº§ä¼ä¸š ç›®å‰æ£‰çº±äº¤å‰²åŽ‚库已ç»ç¡®å®šï¼Œå¦‚图表49所示,指定交割厂库自2017å¹´12月1日开始开展棉纱期货交割业务。郑商所在大é‡è°ƒç ”åŸºç¡€ä¸Šï¼Œæ ¹æ®æ£‰çº±è´¸æ˜“æµå‘å’ŒçŽ°è´§è´¸æ˜“ä¹ æƒ¯ç¡®å®šäº†äº¤å‰²åŽ‚åº“å¸ƒå±€ï¼Œå³åœ¨æ£‰çº±ä¸»äº§é”€åœ°å±±ä¸œã€æ²³å—ã€æ±Ÿè‹åŠæµ™æ±Ÿè®¾ç«‹äº¤å‰²åŽ‚库。河å—ã€å±±ä¸œå’Œæ±Ÿè‹çš„棉纱交割厂库å‡è´´æ°´ä¸º0å…ƒ/å¨ï¼Œæµ™æ±Ÿçš„棉纱交割厂库å‡æ°´ä¸º380å…ƒ/å¨ã€‚棉纱交割厂库仓储费为2å…ƒ/å¨Â·å¤©ï¼ŒæŒ‡å®šè´¨æ£€æœºæž„为河å—çœçººç»‡äº§å“è´¨é‡ç›‘ç£æ£€éªŒé™¢å’Œæµ™æ±Ÿçœçººç»‡æµ‹è¯•ç ”究院。 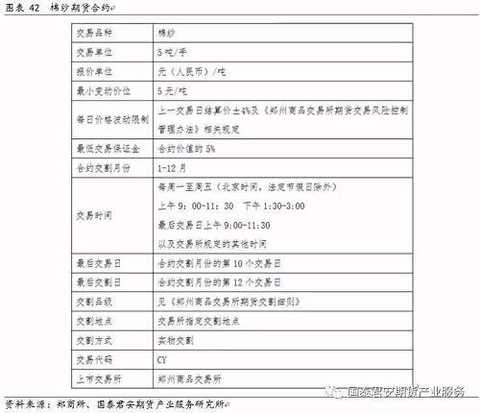
The cotton yarn trading code is CY, taken from the English letter Cottonyarn. In the design of cotton yarn futures contracts, many elements are the same as cotton futures contracts, such as trading units (5 tons / hand), minimum price changes (5 yuan / ton), daily price fluctuation limits, minimum trading margin, final trading delivery day. The exchange is so set up mainly considering that after the cotton yarn futures market, there is a need for upstream and downstream hedging between cotton and cotton yarn, so that investors can more easily grasp and familiarize with cotton yarn futures. 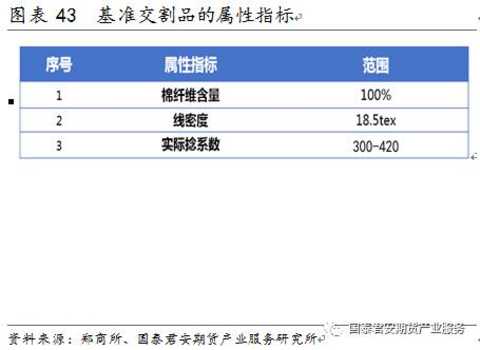

异纤检验方法:通过å¬å¼€è®ºè¯ä¼šã€å‘æ”¾è°ƒç ”é—®å·ã€å®žåœ°åŠç”µè¯è°ƒç ”,市场认为,“试织试染法â€ç¬¦åˆå½“å‰é€šè¡Œçš„检验方法,建议在上市åˆæœŸé‡‡ç”¨è¯¥æ–¹æ³•ï¼›â€œçº±ç–µä»ªæ£€éªŒæ³•â€ä»£è¡¨æœªæ¥çš„检验å‘展方å‘,建议继ç»è·Ÿè¸ªç ”究。 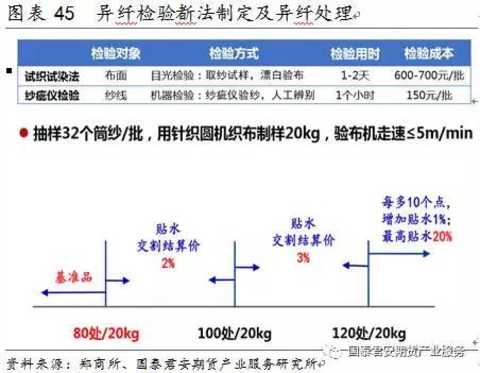
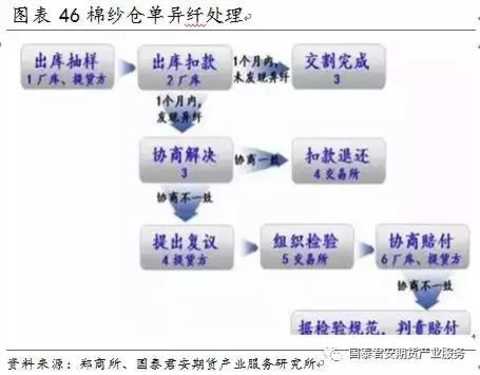
交割å•ä½ï¼š20å¨ï¼ˆå…¬å®šé‡é‡ï¼‰ï¼Œæ£‰çº±æœŸè´§äº¤æ˜“å•ä½ä¸º5å¨/手,交割å•ä½æ˜¯4手棉纱期货。æ¤å¤–,郑商所规定棉纱1交割å•ä½åº”满足“åŒä¸€ç”Ÿäº§åŽ‚家ã€åŒä¸€ç”Ÿäº§æ‰¹æ¬¡â€è¦æ±‚。一是与现货贸易主æµè¿è¾“æ–¹å¼ç›¸åŒ¹é…,便于买方æ货,组织交割;二是与规模以上消费ä¼ä¸šçš„ç”Ÿäº§è´¸æ˜“ä¹ æƒ¯ç›¸é€‚åº”ï¼Œå¸å¼•ä¹°æ–¹å‚与交割。 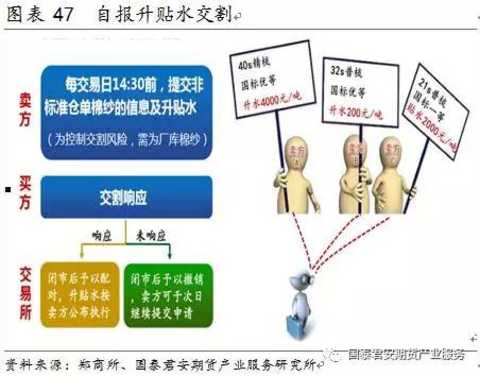
Ningbo Liyuan Garment , https://www.liyuangarment.com